
Benchmark cpu how to#
Running this much smaller snippet on a cycle-accurate simulator can give clues on how to improve performance. For example, if a benchmark extracts the key algorithms of an application, it will contain the performance-sensitive aspects of that application. While application benchmarks usually give a much better measure of real-world performance on a given system, synthetic benchmarks are useful for testing individual components, like a hard disk or networking device.īenchmarks are particularly important in CPU design, giving processor architects the ability to measure and make tradeoffs in microarchitectural decisions. Application benchmarks run real-world programs on the system.
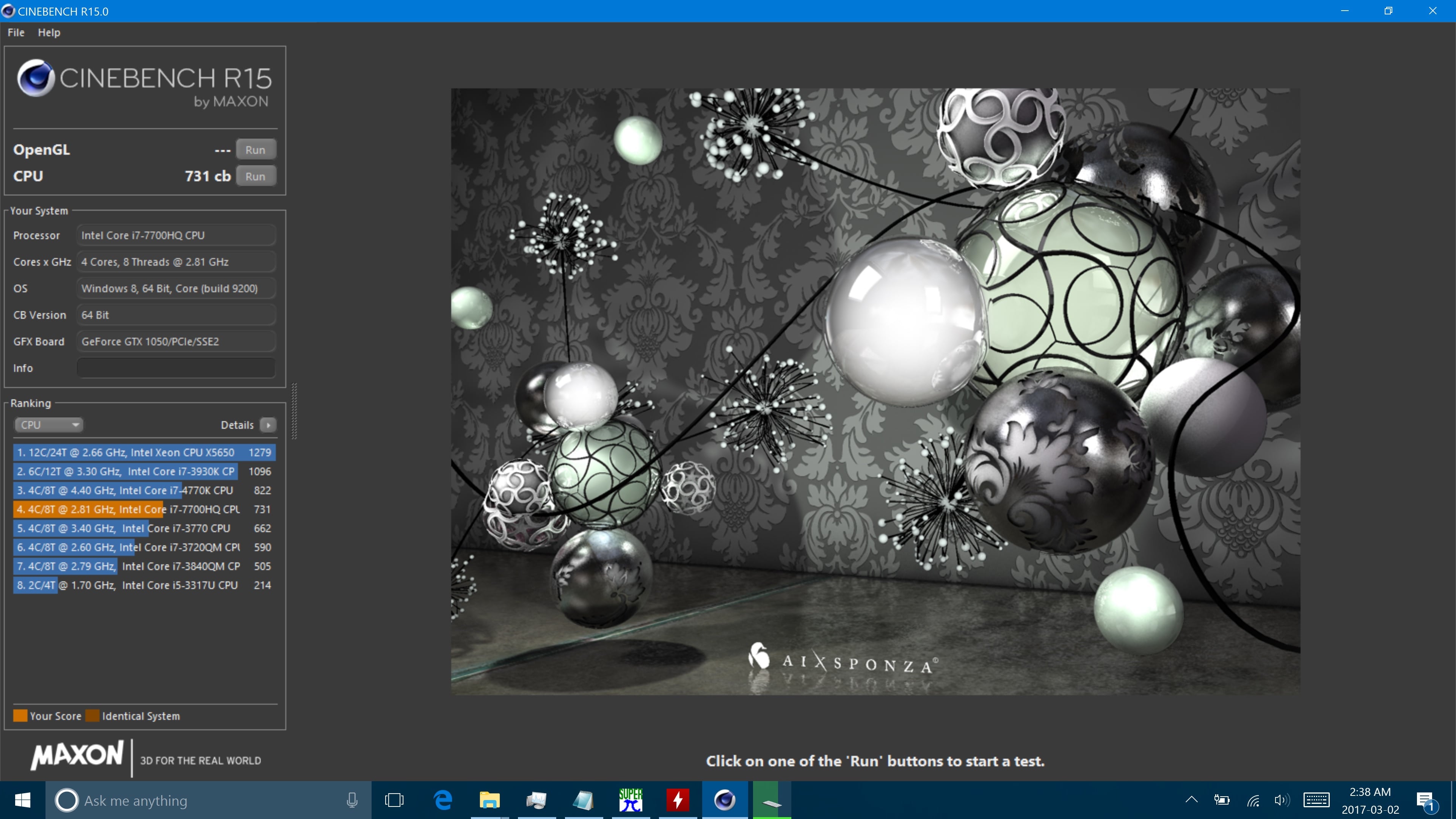
Synthetic benchmarks do this by specially created programs that impose the workload on the component. See BogoMips and the megahertz myth.īenchmarks are designed to mimic a particular type of workload on a component or system.

For example, Pentium 4 processors generally operated at a higher clock frequency than Athlon XP or PowerPC processors, which did not necessarily translate to more computational power a processor with a slower clock frequency might perform as well as or even better than a processor operating at a higher frequency. Therefore, tests were developed that allowed comparison of different architectures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
